Employability refers to your array of skills, knowledge, and personal attributes that enable you to achieve successful employment and thrive in the workplace. It’s about being prepared and adaptable to navigate the labor market throughout your career.
With employability, you possess the essential toolkit that not only lands you a job but also supports career advancement and the ability to transition between roles effectively.
You’ll find that employability encompasses not just the technical abilities specific to a certain job but also the soft skills that are valued across various industries.
These transferable skills, such as communication, teamwork, and problem-solving, are crucial in making you an impactful employee.
Key components of employability
a) Employability skills
Employability skills, often referred to as ‘soft skills,’ are the non-technical attributes that you bring to the job.
These include:
- Critical thinking: The ability to analyze situations and make well-reasoned decisions.
- Communication: Effective verbal and written skills which are essential for conveying ideas and working with others.
- Teamwork: Collaborating with others to reach common goals.
- Organization: Keeping yourself and your tasks well-structured and planned.
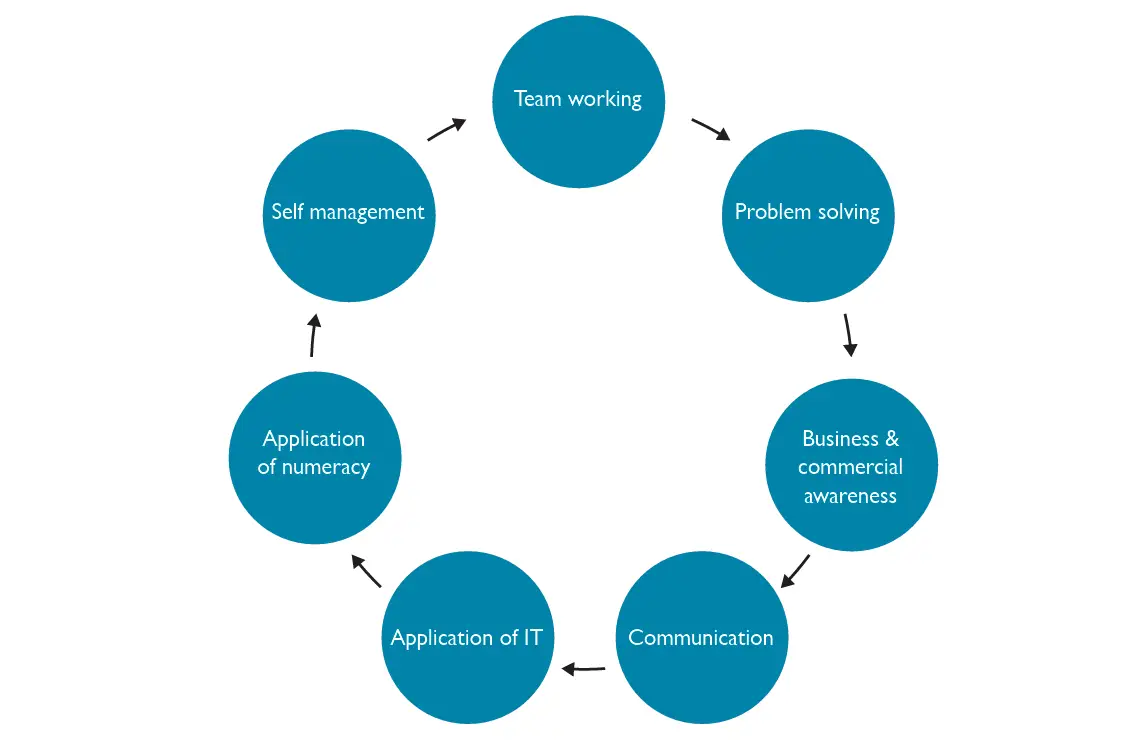
These skills are transferable across industries and roles, making them highly valued by employers.
b) Personal qualities and attitudes
Your personal traits can significantly impact your employability.
Desirable qualities include:
- Initiative: Showing readiness to undertake work beyond your job description proactively.
- Enthusiasm: Demonstrating genuine interest and eagerness in your field or role.
- Positive attitude: Maintaining a constructive outlook, even in challenging situations.
- Reliability: Being dependable, punctual, and trustworthy.
A positive attitude and reliability are often the most cited qualities employers look for, as they contribute to a positive work environment and consistent performance.
c) Knowledge and technical skills
Technical skills and knowledge are specific abilities and know-how that relate to the tasks of a particular job. These can include:
- Knowledge: Mastery of subject matter related to your field.
- Technical skills: Proficiency with specialized tools or software.
For example, computer skills are increasingly crucial in virtually all job sectors due to the digitalization of the workplace. Acquiring relevant technical skills could be a deciding factor in your employability.
Career development and employability
Employability encapsulates your ability to gain initial employment, maintain employment, and obtain new employment if required.
In the context of career development, employability is the bridge between what you learn and how you apply that knowledge to establish and advance in your career.
Career management skills
You need a robust set of career management skills to navigate successfully in the labor market. These skills include career planning, understanding labor market trends, and ongoing professional development.
Begin by setting specific, measurable goals and crafting a career action plan. Your self-management capabilities also play a critical role, enabling you to adapt to change and take decisive action towards your career advancement.
Keep your resume and cover letter updated to reflect your skills accurately and participate in internships to gain practical experience.
Transitioning into the workforce
Graduate employability is more than just academic achievement; it’s about making a seamless transition into the workforce.
Familiarize yourself with the expectations of the world of work, which values not just what you know, but also the practical application of this knowledge.
Networking, gaining relevant work experience, and understanding the nuances of job application processes, such as tailoring your resume for different jobs, will aid in this transition.
Remember that every internship or part-time job is an opportunity to build skills essential for your graduate employability.
Improving employability in education
When it comes to paving the way for a robust career, your employability is a pivotal factor. This is largely influenced by the quality of education and the skills you acquire during your time on campus.
The curriculum in higher education should equip you with the necessary academic skills, while also preparing you for ongoing professional development.
Curriculum integration
Your curriculum should not be a static store of knowledge, but a dynamic framework that integrates business-relevant skills.
For instance, courses should include case studies where real-world business scenarios are analyzed, allowing you to apply theoretical knowledge in a practical context.
This bridges the gap between education and industry demand, enabling you to build a portfolio of skills that are directly applicable to the workplace.
Lifelong learning and continuous development
Today, continuous learning is not just encouraged; it’s expected.
To remain competitive, you must embrace lifelong learning as a core tenet of your personal and professional life.
This might involve engaging in periodic professional development workshops, online courses, or even pursuing further higher education qualifications.
Cultivating a habit of learning keeps your skills sharp and your knowledge relevant, ensuring that your employability extends well into the future.
Employability FAQs
How do authors typically define the concept of employability?
Authors often define employability as a set of achievements, understandings, and personal attributes that make individuals more likely to gain employment and be successful in their chosen occupations.
This takes into account both the personal outcome of educational processes and the skills required in various workplaces.
What are some practical examples that illustrate employability?
Practical examples of employability might include efficiently collaborating on a team project, proactively learning new technology pertinent to your field, or successfully managing your time to meet and exceed work deadlines.
What strategies can students employ to develop their employability skills?
Students can develop their employability skills by participating in internships, volunteer work, or role-playing simulations. Such experiences enable them to practice communication, teamwork, and other relevant skills in real-world settings.
Conclusion
Understanding and enhancing your employability is a continuous process. It goes beyond acquiring a set of qualifications; it’s about personal and professional development that never truly ends.
In the ever-evolving labor market, staying employable means remaining curious, actively learning, and continuously adapting to new challenges and opportunities.


